- …



- …

The Signal Science Lab
Dream, Innovate, Deliver
It all begins with an Idea!
The lab works on the philosophy of “using science to serve community”. Our motto is to “Invent Future". The Lab members pursue high risk projects and believe that if “one is not failing, one is not trying hard enough”. The success of the projects is measured on practical outcomes, such as the number of start-ups and licensing agreements originated from the research projects.
About Us
A modern innovation lab with multidisciplinary research focus on the problems that need urgent solutions from disease dignosis to data compression to anything under the sun.
The lab pursues a synergistic interface among the disciplines of Computer Science, Electrical Engineering, Economics, Physical Sciences and Life Sciences.
The fundamental and applied research carried out in the lab is aimed at technology development and commercialization, following the “lab-to-market” approach to address unmet societal needs.
What's New
Alumni Highlight

Nimesh Srivastava
Co-founder and CEO, EZ Diagnostics
Inventing New Algorithms to Speed Up MRI Scan Time
Research Areas
1Electron Spin Resonance
2Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
4Materials Design
5Video Processing
6Signal Processing
7Molecular Biophysics
8Magnetic Resonance Imaging
9Clinical Diagnosis
12Forensics
Research Projects

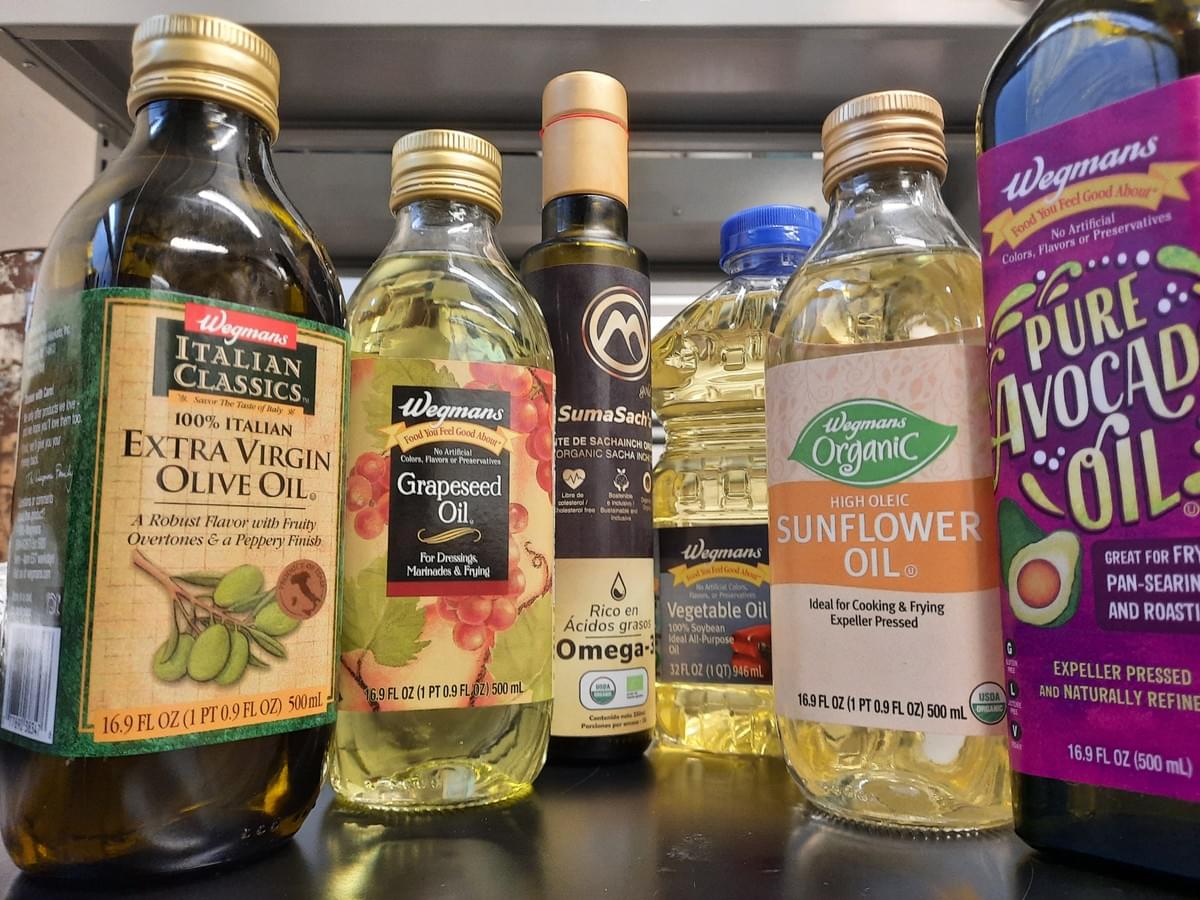
Improving Shelf Life of Edible Oil
Quality Control
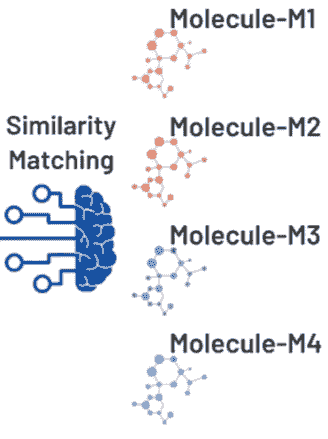
Identifying Unknown Molecules in a Mixture
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance

Enabling Ayurvedic Medicine for Wider Use
Quality Control
Making Electricity Reliable and Affordable
Energy Security

Developing Digital Fingerprint for Videos
Video Processing
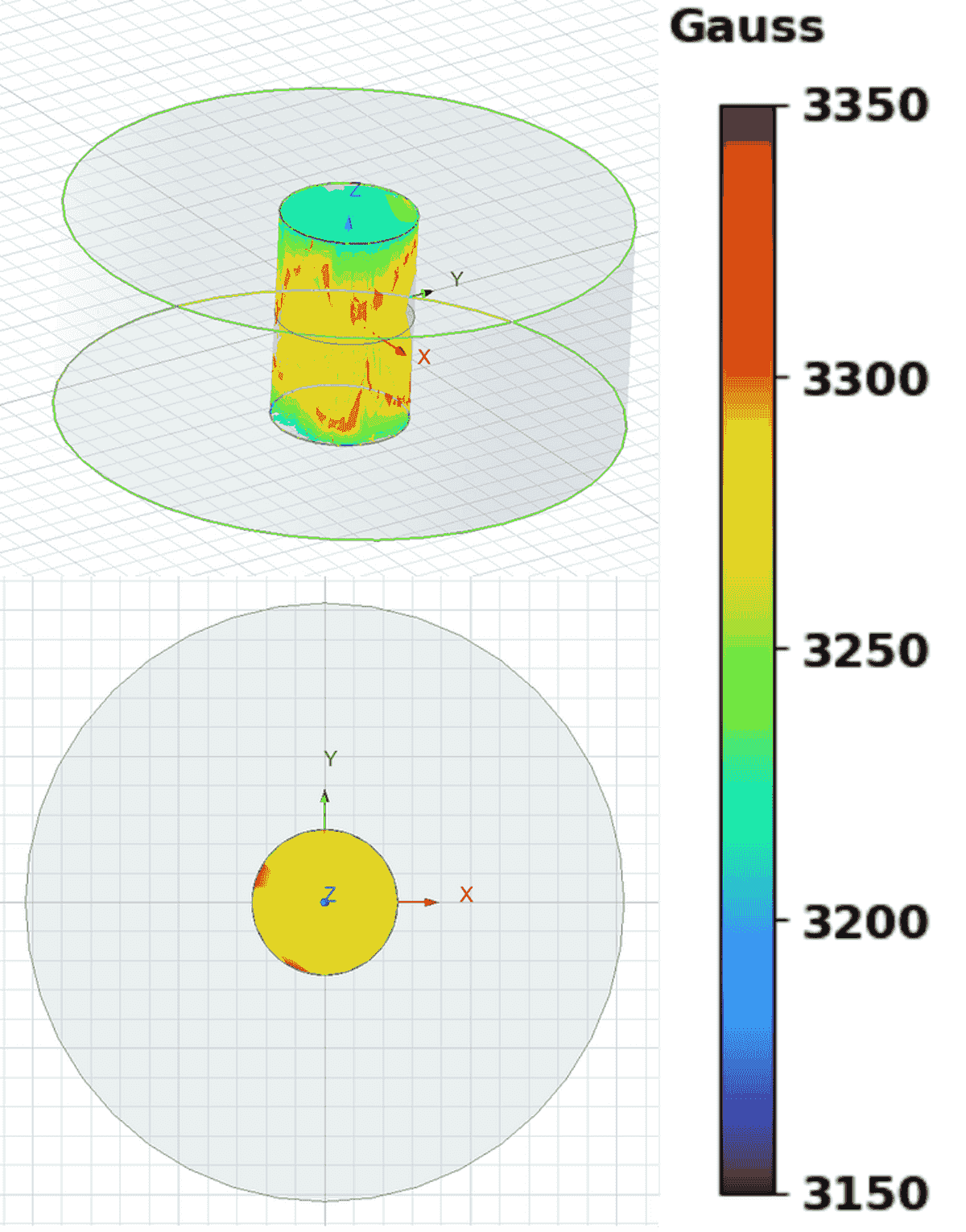
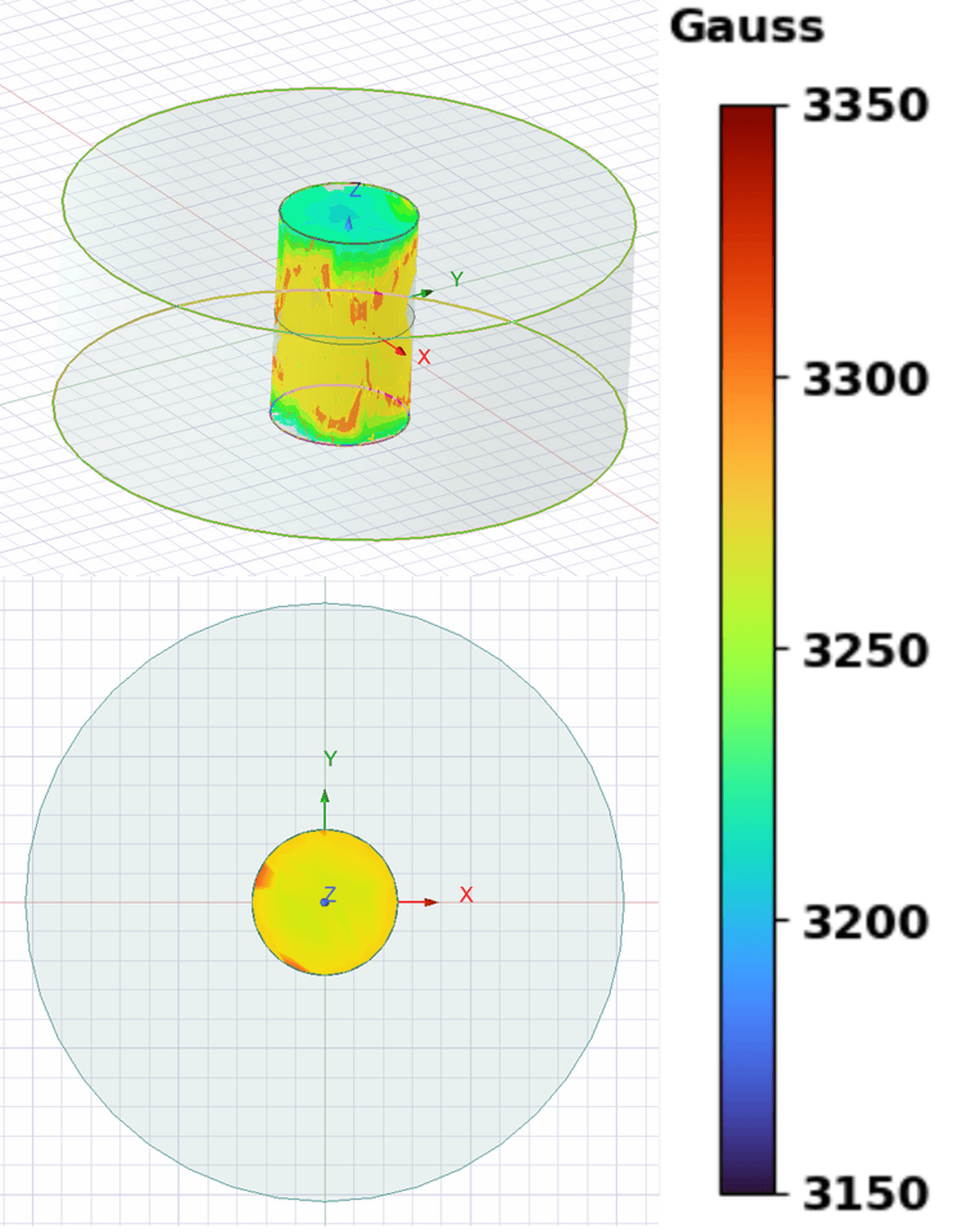
Designing Miniaturized Low Cost Magnet
National Security
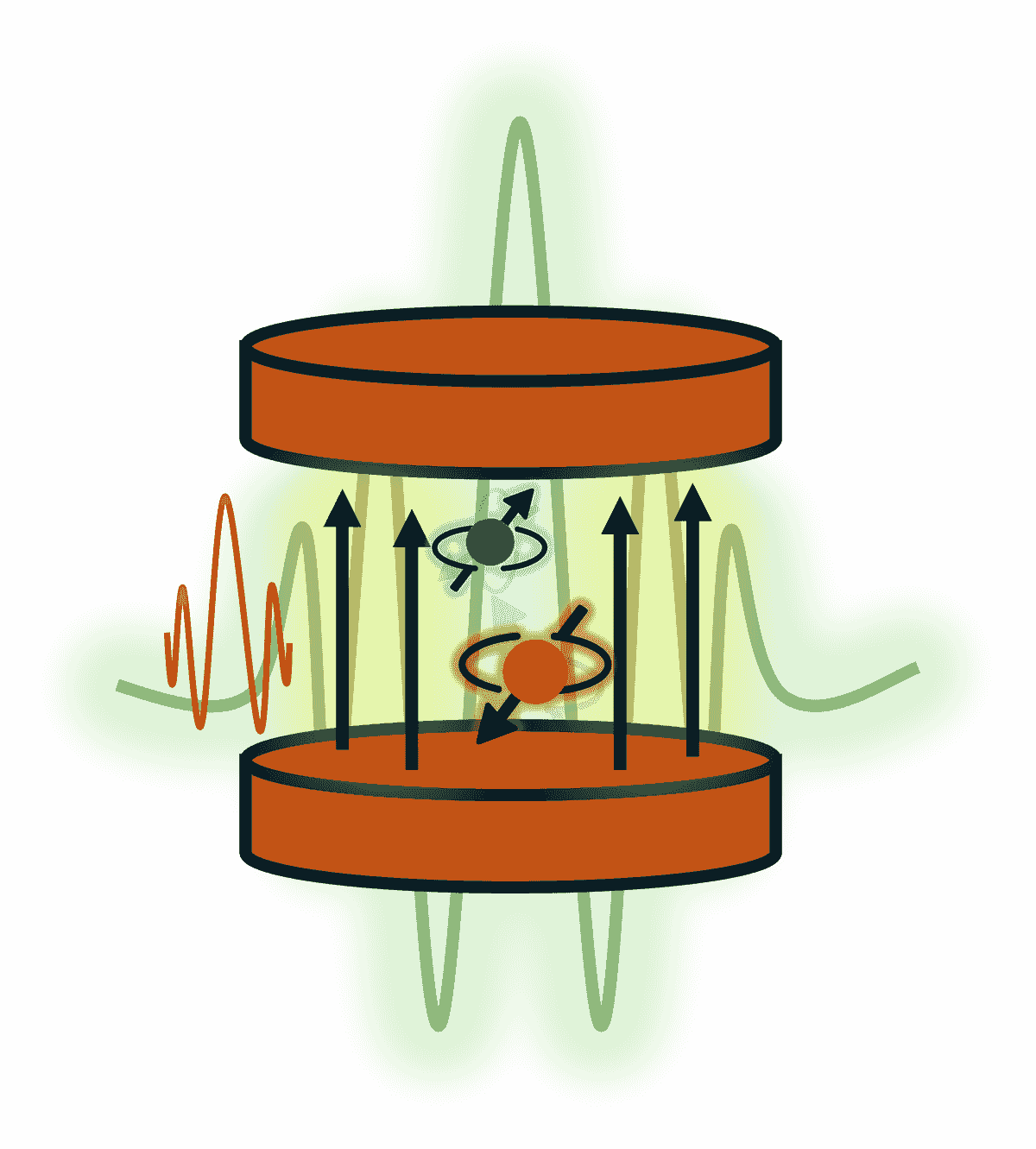
Designing New Instrumentation for ESR
Electron Spin Resonance
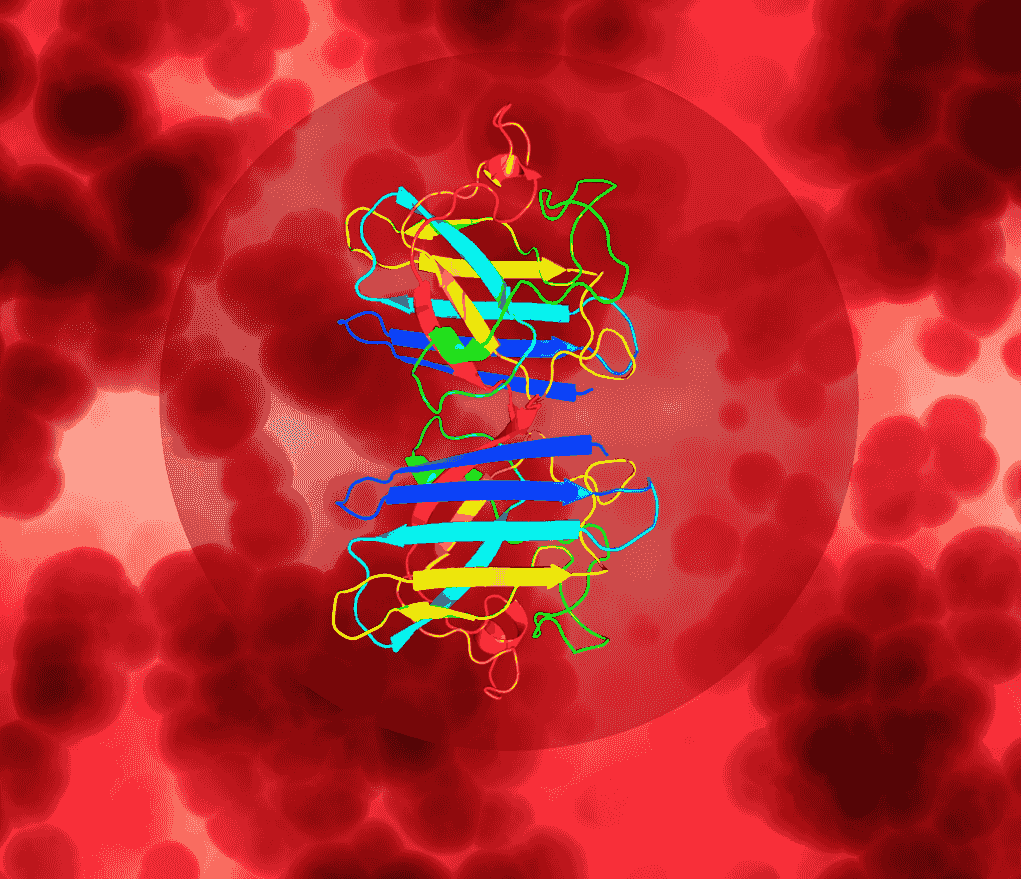
Detecting ALS via Blood Test
Disease Diagnosis

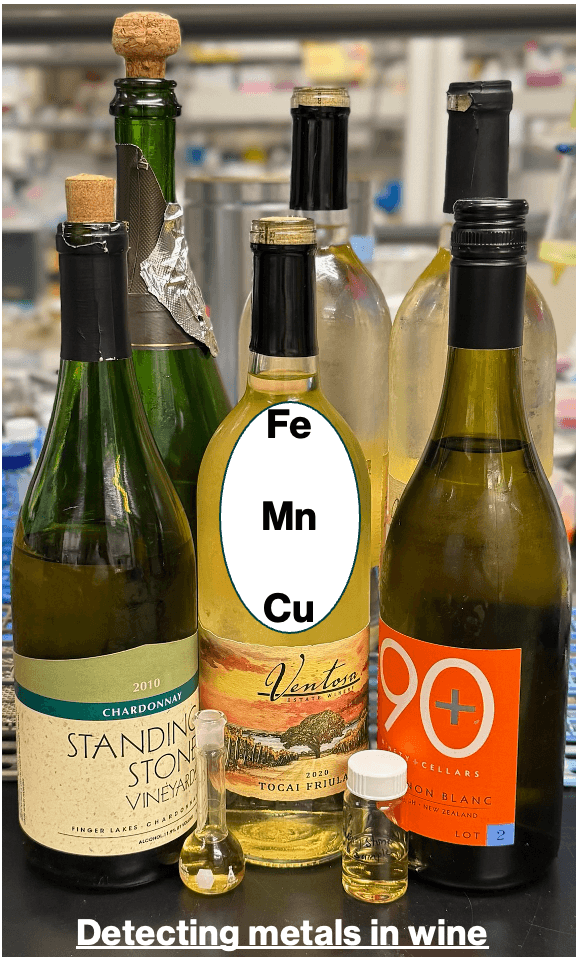
Avoiding Wine Turning into Vinegar
Quality Control
Lab Culture
In the lab, the post-docs, graduate students and undergraduate students design research projects based on their own ideas. While common for post-docs and graduate students, undergraduate students also serve as first authors in publications as they independently work on their research projects. The lab environment is extremely collaborative where technical skills and experiences are constantly shared by the lab members.